Surprising Causes of Epididymitis: Beyond STDs
Introduction
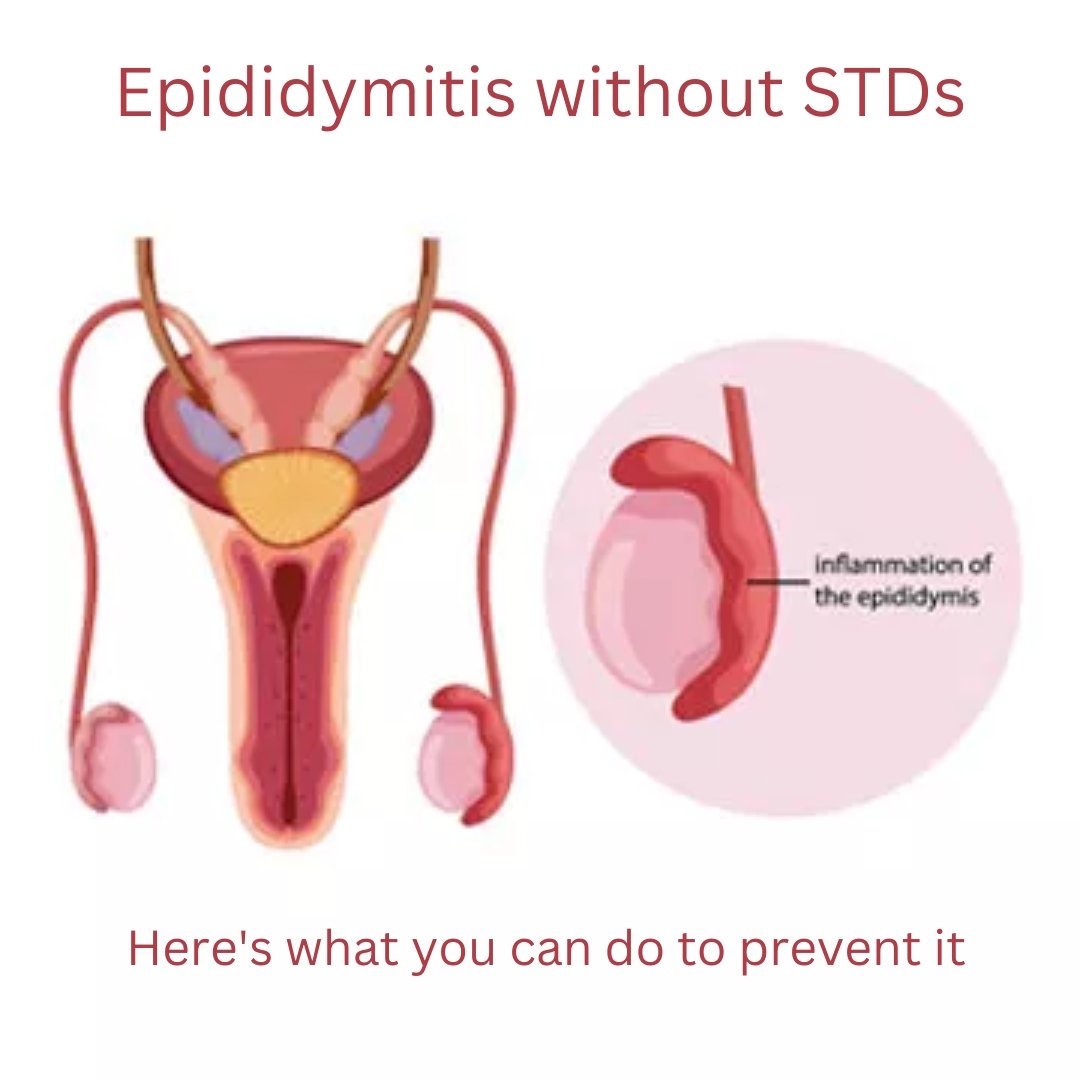
When most people hear about epididymitis, they immediately think of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). However, there are several surprising ways you can develop this painful condition without any sexual contact. In this article, we’ll explore five shocking ways you can get epididymitis without an STD, shedding light on the lesser-known causes of this uncomfortable ailment.
Physical Trauma
One of the most unexpected ways to develop epididymitis is through physical trauma to the testicles or groin area. This can include:
- Sports injuries
- Accidents
- Tight-fitting clothing
- Prolonged sitting or cycling
Physical trauma can cause inflammation in the epididymis, leading to pain, swelling, and discomfort. It’s important to protect your groin area during physical activities and avoid prolonged pressure on the testicles.
Urinary Tract Infections
Contrary to popular belief, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can cause epididymitis without the involvement of an STD. In fact, epididymitis without an STI or UTI is less common than cases linked to urinary tract issues. UTIs can occur due to:
- Poor hygiene
- Dehydration
- Holding urine for extended periods
- Kidney stones
When bacteria from a UTI travel up the urinary tract, they can reach the epididymis and cause inflammation. Proper hydration and regular bathroom breaks can help prevent UTIs and reduce the risk of epididymitis.
Medication Side Effects
Believe it or not, certain medications can lead to epididymitis as a side effect. Some drugs that have been associated with this condition include:
- Amiodarone (used for heart rhythm disorders)
- Hydralazine (used for high blood pressure)
- Certain antibiotics
If you’re taking any of these medications and experience symptoms of epididymitis, consult Dr. Mongas immediately. They may need to adjust your treatment plan or explore alternative options.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders can cause the body’s immune system to attack healthy tissues, including the epididymis. Some autoimmune conditions that may lead to epididymitis include:
- Behçet’s disease
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
While these cases are rare, it’s essential to be aware of the possibility, especially if you have a history of autoimmune disorders. Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider can help manage these conditions effectively.
Rare Infections
While STDs are the most common infectious cause of epididymitis, other rare infections can also lead to this condition. These include:
- Tuberculosis
- Brucellosis
- Fungal infections
These infections are more likely to occur in individuals with weakened immune systems or those who have traveled to areas where these diseases are more prevalent. If you’ve recently traveled and experience symptoms of epididymitis, inform your doctor about your travel history.
Conclusion
Understanding the various causes of epididymitis beyond STDs is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While the recovery time for epididymitis can vary depending on the cause, most cases improve within a few weeks with appropriate care. It’s important to note that while epididymitis primarily affects males, females can experience similar symptoms in the fallopian tubes, a condition known as salpingitis.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of epididymitis, such as testicular pain, swelling, or discomfort, don’t automatically assume it’s caused by an STD. Consult your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can lead to faster recovery and prevent complications.
Have you or someone you know experienced epididymitis from a non-STD cause? Share your story in the comments below to help raise awareness about this often misunderstood condition.
Learn more about urinary tract health and prevention
Discover ways to protect yourself from sports-related groin injuries
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.










Leave a Reply