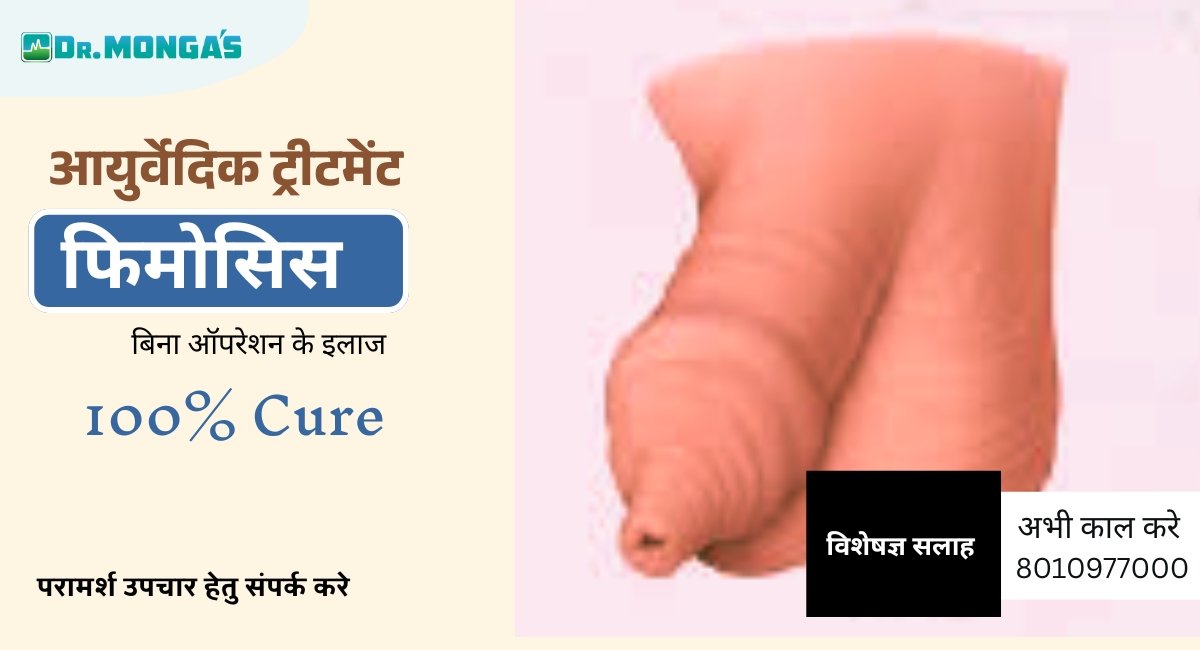
What Is Phimosis? Phimosis is a condition where the foreskin of the penis cannot be retracted. While it’s common in infants and young boys due to the natural attachment of the foreskin to the glans (head) of the penis, it usually resolves on its own. However, in some cases, phimosis can persist into adulthood, potentially causing complications if left untreated.
Types of Phimosis
Phimosis can be categorized into two primary types:
Congenital Phimosis
Congenital phimosis is present at birth and is often a natural occurrence in infants. As mentioned earlier, it usually resolves as the child grows, with the foreskin becoming more flexible and retractable over time. In most cases, medical intervention is unnecessary, unless complications arise.
Acquired Phimosis
Acquired phimosis occurs later in life and can be caused by factors such as infections, inflammation, or scarring from trauma. Conditions like balanitis (inflammation of the glans) and lichen sclerosus can also contribute to acquired phimosis, causing discomfort and other related issues.
Symptoms and Recommended Tests for Phimosis
Symptoms of phimosis may vary depending on its severity. Common signs include:
- Difficulty retracting the foreskin, particularly during erections or sexual activity
- Pain or discomfort in the penile region
- Swelling or redness of the foreskin or glans
- Recurrent infections, irritation, or inflammation
Diagnosis
Diagnosing phimosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The clinician will assess the foreskin’s ability to retract and may inquire about any associated symptoms. In certain cases, further tests may be required to rule out underlying conditions contributing to the phimosis.
The Link Between Phimosis and Erectile Dysfunction
The relationship between phimosis and erectile dysfunction (ED) is complex, and several factors can contribute to this connection:
Physical Discomfort and Pain
Men suffering from phimosis may experience physical discomfort or pain during erections. This discomfort can lead to anxiety about sexual performance and, ultimately, an aversion to sexual activity, which may manifest as erectile dysfunction.
Infections and Inflammation
Acquired phimosis can result in inflammation or infections, which, in turn, can affect erectile function. Chronic inflammation may lead to scarring or narrowing of the urethra, affecting urinary flow and contributing to difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection.
Psychological Impact
The psychological impact of phimosis should not be underestimated. Difficulty retracting the foreskin or concerns about pain during sex can lead to stress and emotional distress. These factors are often linked to erectile dysfunction. Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of phimosis is crucial for overall sexual health.
Reduced Sensitivity
Phimosis may also lead to altered sensitivity during sexual activity. A tight foreskin can cause reduced sensation in the glans, leading to difficulties in achieving the same level of sexual pleasure as men without this condition. This variation can negatively affect sexual performance and confidence, further contributing to erectile dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Phimosis
There are various treatment options available for managing phimosis.
Non-Surgical Treatment
In mild cases of phimosis, non-surgical treatments may be effective. These include:
- Topical Steroids: Doctors may prescribe steroid cream to help soften the foreskin and promote retraction.
- Gentle Stretching Exercises: Gradual and gentle stretching of the foreskin can sometimes help to alleviate tightness over time.
Surgical Treatment
When non-surgical methods are ineffective or if phimosis causes severe complications, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical options include:
- Circumcision: The removal of the foreskin is a permanent solution that eliminates the condition entirely.
- Preputioplasty: A less invasive procedure that involves making incisions in the foreskin to allow for better retraction while preserving the foreskin itself.
Prevention and Self-Care
Preventing phimosis or its complications involves a few proactive measures:
Good Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene of the genital area can help prevent infections that may lead to acquired phimosis. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is essential.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Having routine check-ups with a healthcare provider allows for early detection of any alterations in genital health. This practice can help men address any potential issues before they escalate.
Stress Management
Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques or counseling can help mitigate the psychological components that may contribute to erectile dysfunction related to phimosis.
Conclusion
Phimosis can have varying effects on men, including complications such as erectile dysfunction. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and potential treatment options is crucial for individuals facing this challenge. By prioritizing good hygiene, regular medical check-ups, and addressing psychological impacts, men can take proactive measures to protect their sexual health and well-being.
“Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers and partners is essential for navigating the complexities of phimosis and erectile dysfunction.”










Leave a Reply