Understanding the initial signs of HIV is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, and if left untreated, it can lead to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Recognizing the early symptoms can lead to timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Early detection not only allows for better health outcomes but also reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
HIV is a virus that specifically targets the immune system, weakening the body’s natural defenses against illnesses. Unlike some other viruses, the human body cannot completely eliminate HIV, which means that once a person is infected, they have it for life. The virus primarily attacks CD4 cells (T-cells), which are vital for immune response. Over time, as HIV destroys these cells, the body becomes more susceptible to infections and certain cancers. If you’re seeking HIV specialist consultation in Delhi, expert medical care is available.
However, with proper medical care, HIV can be managed, and individuals with HIV can live long, healthy lives. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) has revolutionized the treatment of HIV, allowing individuals to maintain a low viral load and healthy CD4 counts. This not only prolongs life but also reduces the chances of transmitting the virus to others. Understanding HIV and its management is essential for anyone living with the virus or supporting someone who is.
Early Stage HIV Symptoms
The early stage of HIV, known as the acute infection stage, typically occurs two to four weeks after the virus enters the body. This stage is also referred to as acute retroviral syndrome (ARS) or primary HIV infection. During this time, many people experience flu-like symptoms, which are the body’s natural response to the virus. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, often mimicking other viral infections, which can make early detection challenging.
- Fever: A high fever is one of the most common early symptoms of HIV. It is often accompanied by other mild symptoms such as fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and a sore throat. The fever is typically persistent and may be accompanied by night sweats, which can be severe and disruptive to sleep.
- Fatigue: The inflammatory response generated by your immune system can also cause you to feel tired and lethargic. Fatigue can be both an early and later symptom of HIV. This exhaustion can interfere with daily activities and may not be relieved by rest or sleep, indicating a deeper systemic issue.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Lymph nodes, part of your body’s immune system, often become inflamed and swollen as your body fights off infections. This swelling is commonly seen in the neck, armpits, and groin and can be tender or painful to the touch. The lymph nodes are an essential part of the immune defense, and their enlargement indicates active immune engagement.
- Sore Throat and Headache: These are common symptoms that occur during the acute infection stage. They may be mistaken for a common cold or influenza but are typically more persistent and severe. A sore throat may be accompanied by a persistent dry cough that doesn’t respond to usual remedies.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Many people experience aches and pains in their muscles and joints during the early stages of HIV. These symptoms can be diffuse and affect various parts of the body, often leading to discomfort and decreased mobility. Such pain is due to the body’s immune response to the viral invasion.
- Skin Rash: One of the most notable early signs of HIV is a skin rash. The rash usually appears as flat or slightly raised red spots on the skin, and it can occur in various parts of the body. It may be accompanied by itching, and its appearance can vary, sometimes resembling other dermatological conditions, which can complicate diagnosis.

What is Usually the First Sign of HIV?
While the symptoms mentioned above can occur early on, the very first sign of HIV can vary from person to person. Often, the first noticeable sign is a fever. This fever is the body’s response to the virus entering the bloodstream and the immune system’s activation. It acts as an early warning system, signaling that the body is under attack and that medical attention may be necessary. To learn more about diagnosis and treatment, visit our HIV-1 & HIV-2 Treatment Page.
Read More : Understanding AIDS: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
The Role of Fever in Early HIV Symptoms
The fever associated with early HIV infection is usually persistent and can be quite high, often reaching over 100°F (38°C). It may be accompanied by other mild symptoms, making it easy to mistake for the common cold or flu. This is why it’s important to consider the context of potential exposure to HIV when experiencing such symptoms. If there is any suspicion of HIV exposure, seeking medical advice and testing is crucial.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of HIV is critical for several reasons:
- Preventing Transmission: Knowing your HIV status helps prevent the spread of the virus to others. With early diagnosis, individuals can take precautions to protect their partners. This includes practicing safer sex, using protection, and, in some cases, taking pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent transmission.
- Access to Treatment: Early treatment can dramatically improve health outcomes. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) can help keep the virus under control and maintain a healthy immune system. Starting treatment early reduces the viral load to undetectable levels, significantly lowering the risk of transmission and improving long-term health outcomes.
- Improved Quality of Life: Starting treatment early can lead to a longer, healthier life and reduce the risk of developing AIDS. Early intervention allows individuals to manage HIV as a chronic condition, similar to other long-term illnesses. This management includes regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments to maintain health.
How is HIV Diagnosed?
HIV Testing
HIV is diagnosed through specific tests that detect the presence of the virus in the body. The most common tests include:
- Antibody Tests: These tests look for antibodies that the body produces in response to the virus. They can take a few weeks to months to develop after exposure. Antibody tests are often the first step in HIV screening due to their accessibility and ease of use.
- Antigen/Antibody Tests: These can detect both HIV antibodies and antigens (a part of the virus) in the blood. They can identify the virus sooner than antibody tests. This combination test is a common choice in clinical settings due to its increased accuracy and ability to detect early infection.
- Nucleic Acid Tests (NATs): These tests look for the actual virus in the blood and are usually used when someone has had a high-risk exposure or has early symptoms of HIV. NATs are highly sensitive and can detect the virus within days of exposure, making them invaluable in acute cases.
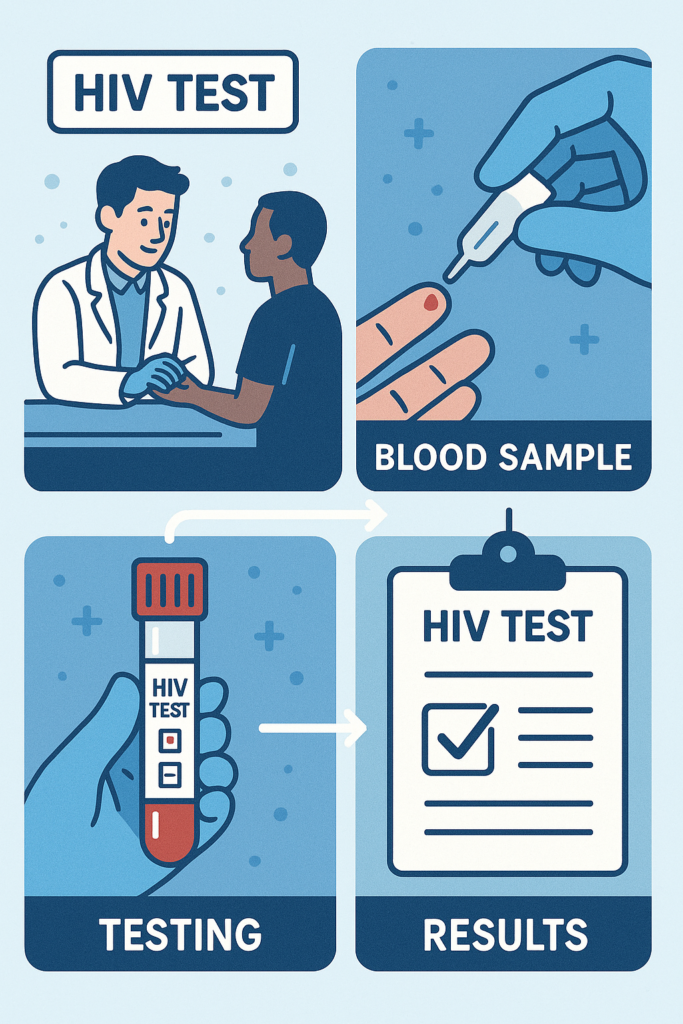
When to Get Tested
If you suspect you’ve been exposed to HIV or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to get tested as oon as possible. Early testing and detection are key to managing the virus effectively. Regular testing is also recommended for individuals with highrisk behaviors, such as having multiple sexual partners or sharing needles. Routine testing can help detect HIV before symptoms appear, ensuring early intervention and better health outcomes.
Managing HIV
Once diagnosed, managing HIV involves a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Regular Medical Care: Frequent check-ups with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring the virus and overall health. Regular blood tests help track viral load and CD4 counts, guiding treatment decisions.
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART): This treatment helps keep the virus under control and prevents the progression to AIDS. Adherence to ART is crucial for maintaining an undetectable viral load and preventing resistance.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco and recreational drugs can support the immune system. These lifestyle changes can enhance treatment effectiveness and improve overall well-being.
- Mental Health Support: Living with HIV can be challenging, and emotional support or counseling can be beneficial. Psychological support helps in coping with the diagnosis and managing stress, anxiety, or depression that may accompany the condition.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of HIV, such as fever and rash, is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect you may have been exposed to HIV, it is important to seek testing promptly. With the right care and management, individuals with HIV can lead fulfilling lives. Always consult healthcare professionals for advice tailored to your specific situation.
Remember, early detection and treatment are your best allies in managing HIV and maintaining your health. Stay informed and proactive about your health to ensure the best possible outcomes. By understanding the disease, accessing treatment, and making informed health choices, individuals with HIV can achieve longevity and quality of life comparable to those without the virus. We are the india’s leading speaclist help you cure HIV at early stage call to book appointment 8010977000









Leave a Reply